
Figure 1-1: Social Emotional Learning
Have you ever experienced difficulty setting goals or making decisions? How do you manage your emotions? Or get along with — and empathize with — others? All of these are crucial social and emotional competencies.
Social-emotional learning (SEL)is the development and implementation of social and emotional skills. SEL is also known as socio-emotional learning and social-emotional literacy. It is the process of building self-awareness, self-control, and social skills that are important for success in school, work, and life.
People who are emotionally and socially well-rounded can better deal with stress, form healthy bonds with others, and make rational choices. SEL helps people of all ages do well in school and life. SEL is a set of skills that can be taught and learned at any age, from preschool on up. This is significant because it is a learned skill that does not come naturally to everyone. Schools can play an essential role in assisting students in developing such skills. It’s crucial to understand that some students might require specialized support to gain the full benefits of SEL.
In this article, we’ll explore the importance of SEL, its benefits, and practical tips for integrating social-emotional learning into the classroom and at home.
- Understanding the Core Components of Social-Emotional Learning
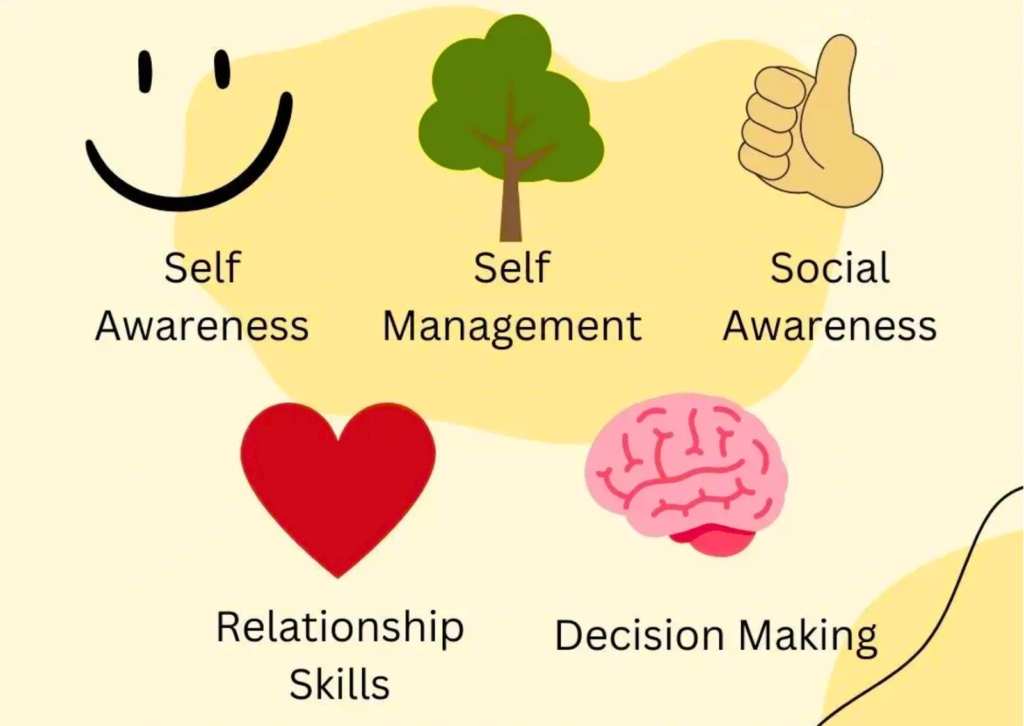
Figure 1-2: 5 Core Components of Social-Emotional Learning
SEL encompasses five key competencies that contribute to emotional intelligence and well-being:
- Self-awareness
Self-awareness refers to recognizing and understanding one’s emotions, strengths, weaknesses, values, and aspirations. It involves accuratelyassessingone’s feelings, thoughts, and behaviors and understanding how they influence personal experiences and choices.
Developing self-awareness enables individuals to recognize their emotional triggers and respond more effectively to various situations. It also promotes self-confidence, self-esteem, and a strong sense of personal identity.
- Self-management
Self-management, also known as self-regulation, involves controlling and managing one’s emotions, thoughts, and behaviors in diverse situations. This competency encompasses impulse control, stress management, self-discipline, and goal-setting.
By developing self-management skills, individuals can better cope with challenges, stay focused on their goals, and maintain a healthy work-life balance. Effective self-management also contributes to emotional resilience and overall well-being.
- Social awareness
Social awareness involves empathy and understanding toward others while appreciating diversity and cultural differences. Thiscompetencyenables individuals to recognize and respect the feelings, perspectives, and needs of others.
Developing social awareness allows for better collaboration and communication in various social settings, including school, work, and community environments. Social awareness fosters belonging, compassion, and inclusivity, promoting positive social interactions and relationships.
- Relationship skills
Relationship skills encompass developing and maintaining healthy relationships through effective communication, cooperation, and conflict resolution. These skills involve active listening, expressing empathy, and respectfully asserting oneself. Building strong relationship skills allows individuals to create meaningful connections with others, work collaboratively, and navigate social situations effectively. In addition, relationship skills contribute to emotional support, personal growth, and a sense of connectedness with others.
- Responsible decision-making
Responsible decision-making is the process of making ethical, constructive choices based on personal and social factors. This competency requires individuals to consider their actions’ consequences, evaluate their impact on themselves and others, and make informed decisions aligning with their values and goals.
Responsible decision-making promotes accountability, problem-solving, and critical thinking. By developing this competency, individuals can navigate complex situations, make better choices, and contribute positively to their community.
2. The Impact of Social-Emotional Learning on Children’s Lives

Figure 2-1: Impacts of SEL on Children’s Life
Numerous pieces of research have shown that social-emotional skill building improves students’ mental and physical health, family relationships, and problem behaviors, which reduces the need for disciplinary action.
According to a 2009 study, social-emotional learning helped 4–14-year-olds regulate their behavior and have better social relationships.
Anotherresearchon 705 students in schools (high-risk) found that early social-emotional learning is a promising approach to increasing reading, writing, and math skills.
Thisstudy of 2012shows that carefully educating children on social and emotional skills reduced harmful behaviors.
Developing strong social-emotional skills has far-reaching benefits for children, including:
- Improved mental health: SEL fosters emotional resilience and self-esteem, reducing the risk of anxiety, depression, and other mental health issues
- Enhanced academic performance: Students with well-developed social-emotional skills tend to excel academically, as they can manage stress, concentrate, and collaborate effectively with their peers.
- Reduced behavioral issues: SEL helps children develop positive coping strategies and problem-solving skills, which can decrease instances of aggression and other risky behaviors.
- Stronger relationships: By cultivating empathy, communication, and conflict-resolution skills, SEL promotes healthier relationships with friends, family members, and teachers.
- Future success: The skills developed through SEL have lifelong applications, contributing to personal and professional success in adulthood.
3. The Far-Reaching Benefits of SEL for Diverse Groups
Schools

Figure 2-2: Benefits of Social-Emotional Learning for Schools
Establishing a safe, socio-emotional school environment enables children to develop essential social skills. SEL promotes emotional intelligence and decision-making, creating a pleasant setting where happier students thrive academically with fewer disciplinary issues.
Families

Figure 3-1: Benefits of Social-Emotional Learning for Families
SEL enhances familial relationships, forming the basis for social and emotional well-being. Targeting emotional skills helps parents bond with their children and fosters mutual understanding. This stable foundation paves the way for success in other life areas.
Communities

Figure 3-2: Social-Emotional Learning Benefits for Community
SEL emphasizes respect, understanding, and embracing diversity. Positive Action’s approach, based on treating others as you wish to be treated, fosterssocial connectionsand a harmonious community. Beyond traditional school settings, SEL benefits social groups of all kinds.
4. Practical Strategies for Implementing Social-Emotional Learning in the Classroom

Figure 4-1: Practical Strategies for Implementing SEL in the Classroom
Teachers can incorporate SEL into their classrooms through various methods:
- Explicit instruction:
Integrate SEL lessons and activities into the curriculum, focusing on the five core competencies. Use age-appropriate materials and teaching methods to engage students.
- Modeling:
Demonstrate social-emotional skills through your behavior, such as expressing emotions appropriately, empathizing with students, and resolving conflicts constructively.
- Creating a supportive environment:
Foster a classroom atmosphere that values diversity, inclusion, and collaboration. Encourage students to share theirfeelingsand experiences and offer support and guidance when needed.
- Reinforcing skills:
Provide opportunities for students to practice SEL skills through role-playing, group projects, and peer feedback. Acknowledge and celebrate their progress and achievements.
- Collaboration with families:
Involve parents and caregivers in the SEL process by sharing information, providing resources, and offering opportunities for them to participate in school activities.
5. Tips for Promoting Social-Emotional Learning at Home

Figure 4-2: Tips for Promoting Social-Emotional Learning at Home
Parents and caregivers play a vital role in nurturing their children’s social-emotional development. Some strategies to promote SEL at home include:
- Create a trusting environment where children feel comfortable discussing their feelings, thoughts, and concerns. Validate their emotions and offerguidancewhen appropriate.
- Demonstrate empathy, problem-solving, and responsible decision-making in your own actions and relationships.
- Establish clear, age-appropriate expectations for behavior and communication, and enforce consequences consistently.
- Encourage children to engage in activities that promote SEL, such as team sports, clubs, or volunteering.
- Maintain open communication with teachers and school staff, and support SEL initiatives in the school setting.
Wrapping Up:
Social-emotional learning (SEL) is a robust educational approach that emphasizes the development of emotional intelligence and well-being in individuals. It targets five core competencies to cultivate healthier relationships, enhance communication, and improve decision-making abilities. By incorporating SEL into various settings, such as classrooms and homes, individuals are better equipped to navigate social situations and achieve personal and professional success throughout their lives. Stay safe and learn more from #1 AAA CE Trainings continuing education training, eetsonline.com/ce.
